Quick Stats
Mozambique
33.64 Million (2024)
$20.95 Billion (2024)
2020
Maputo & Beira
Coal Brics (23%), Petroleum Gas (17%), Aluminium (12%)
Data Source:
- Population and GDP size- World Bank Data – https://data.worldbank.org/indicator
- Trade- OEC- https://oec.world/en/profile/country/
Mozambique occupies a strategic position on Africa’s southeastern seaboard, with more than 2,700 km of coastline and direct overland links to six neighbours, namely: Tanzania and Malawi to the north, Zambia to the northwest, Zimbabwe to the west, and Eswatini and South Africa to the south. It also connects to Botswana through regional trade routes.
23,200 sq
kms
33.64 Million people
Its principal ports, Maputo, Beira and Nacala, are gateways for landlinked nations, serving over 90 million people across Southern and East Africa. Since acceding to the World Customs Organisation’s Revised Kyoto Convention in 2012 and the WTO’s Trade Facilitation Agreement in 2017, Mozambique has signalled its intent to modernise border procedures and reduce bureaucracy.
Anchored to Maputo & Beira Corridors
Nevertheless, infrastructure deficits, customs inefficiencies and limited logistics services continue to restrain growth: the World Bank’s 2023 Logistics Performance Index placed Mozambique 110 of 139 countries, while the final Ease of Doing Business (2019) report ranked it 135 overall.
To capitalise on its coastal and crossborder assets, Mozambique is ramping up sustained investment in transport corridors, port capacity and regulatory reform. TMA’s Mozambique Programme is driving digitalisation, infrastructure upgrading and capacity building to make trade faster, cheaper and more predictable.
Early Milestones
Since 2020
Since October 2020, TMA Mozambique has supported:
Safe Trade Emergency Response (2020–2021)
- Distributed PPE to frontline staff at the Ressano Garcia Border
- Developed and trained 120 officials on Safe Trade Protocols across customs, immigration, health and SPS inspections
Trade Facilitation and Digitalisation (2022–2030) – see below
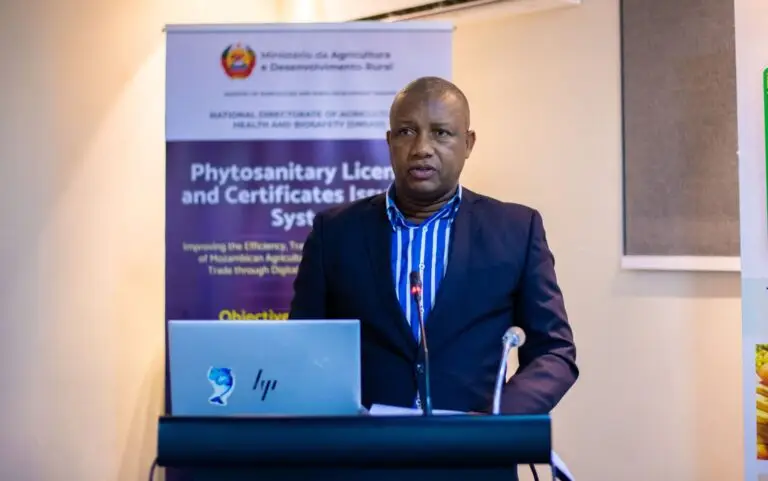
E-Phyto Digitalisation
Implementing an end‑to‑end electronic phytosanitary certification system (funded by Ireland and the Netherlands) to replace the manual, paper‑based process.
Data and Systems Integration
Linking the national single window to the IPPC e‑Phyto hub and introducing online payment, thus reducing transaction errors and opportunities for fraud.
Women and Youth in Logistics
Enhancing the skills of government agencies and the private sector to improve adherence to quality and sanitary/phytosanitary standards.






















