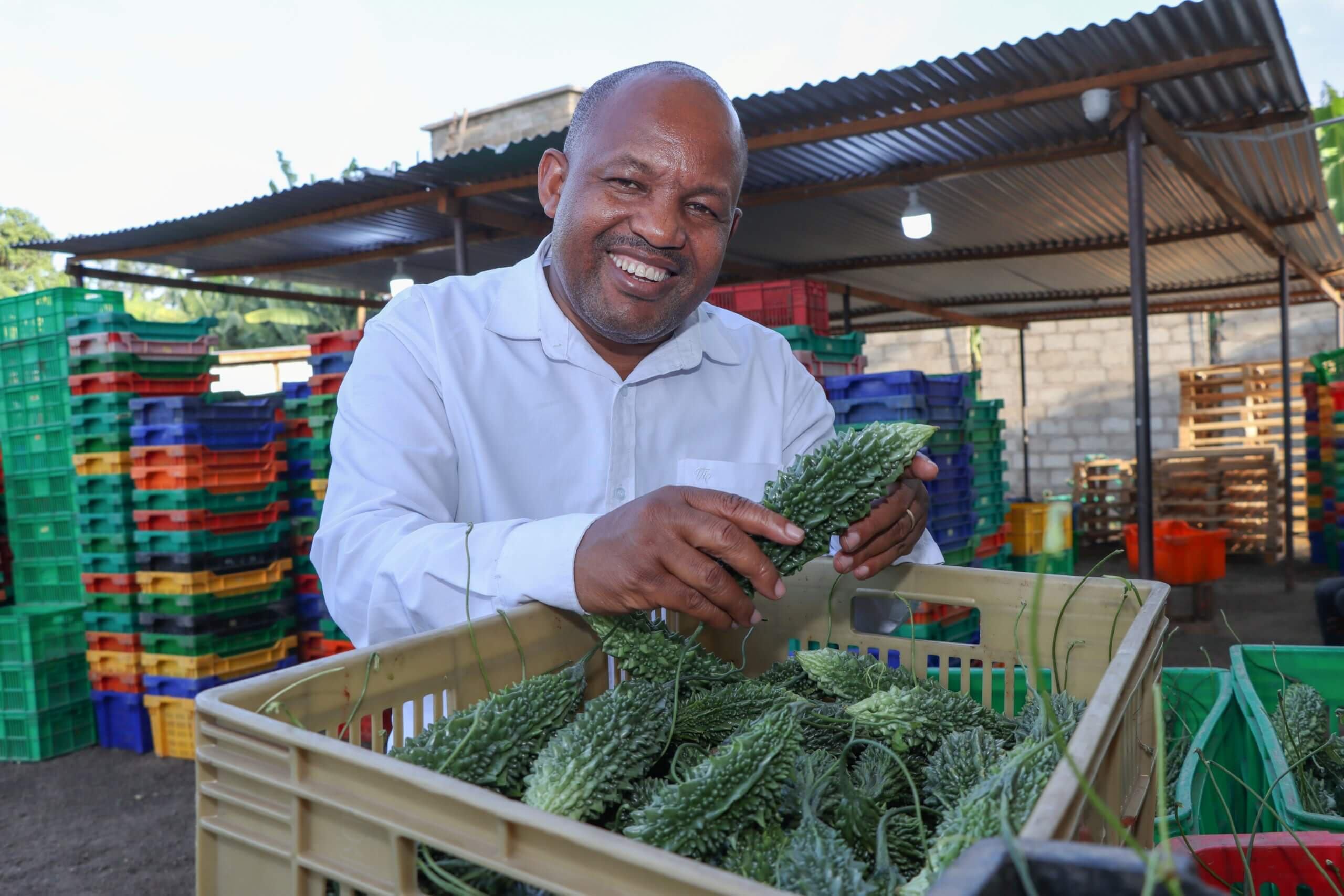
Murang'a County, a significant avocado-producing region in Kenya, contributes 40% of the national output, valued at over $3.5 million. Most homes in the area have small orchards, which have become crucial for rural livelihoods. While cities like Madrid and Stockholm offer lucrative markets for avocados, Murang'a farmers, like others in Kenya, face barriers to entry. These include a lack of understanding of market requirements, international sanitary and phytosanitary (SPS) standards, food safety protocols, and labour conditions. Addressing these challenges requires training and collective effort. Thousands of kilometres away, cities like Madrid and Stockholm represent some of the most lucrative markets for this green gold. But while demand is strong, access remains limited. The farmers of Murang’a, like many of their peers across Kenya, face persistent barriers to entry. Chief among them is inadequate knowledge of market requirements, including compliance with international sanitary and phytosanitary (SPS) standards, food safety protocols, and labour conditions. Bridging this gap demands training, and collective resilience. This was the reason over 60 members of the Lima Linda Cooperative, translated as “Farm and Protect”, assembled for a training session on GLOBALG.A.P. and GRASP protocols in early June 2025. Organised with support from TradeMark Africa (TMA) through the European Union- funded Business Environment and Export Enhancement Programme (BEEEP), the session focused on soil, water, and biodiversity protection, food safety, record keeping, and worker welfare. It marked the fifth group from the cooperative to undergo training since joining the programme in 2024, underscoring the consistency and commitment required for...
How a Kenyan Cooperative is Turning Compliance into a Catalyst for Rural Prosperity
Posted on: June 26, 2025
Posted on: June 26, 2025