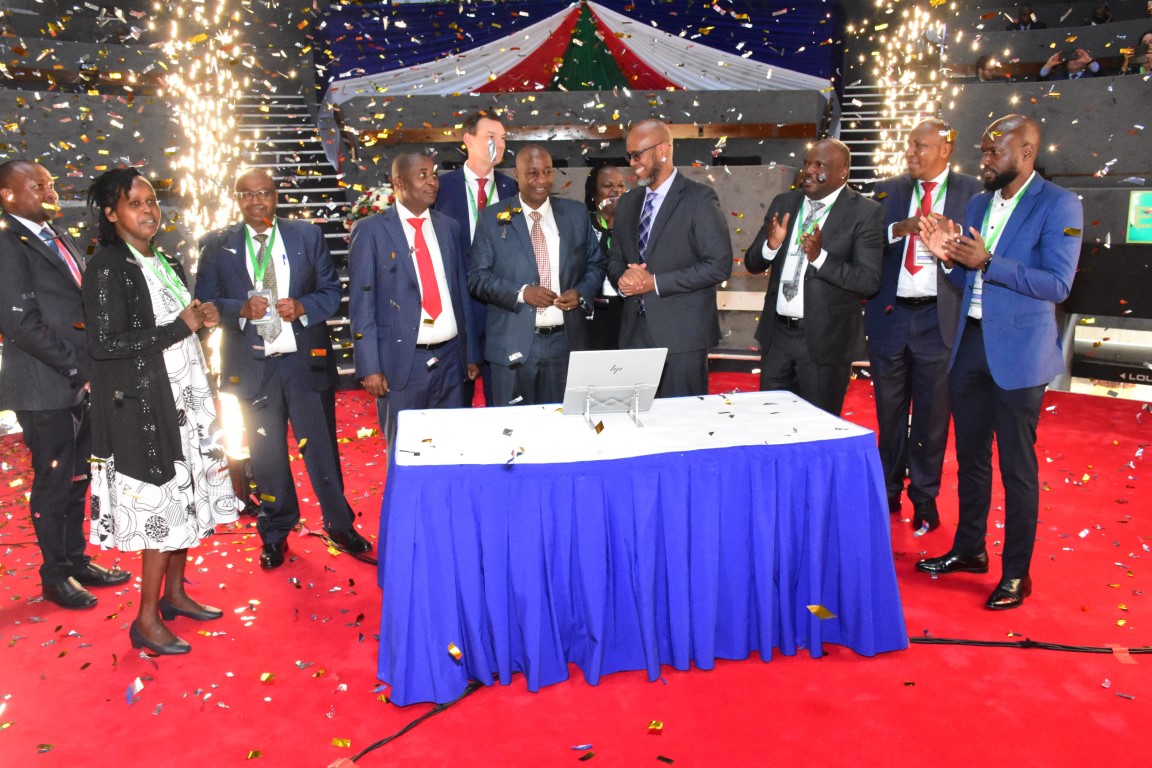
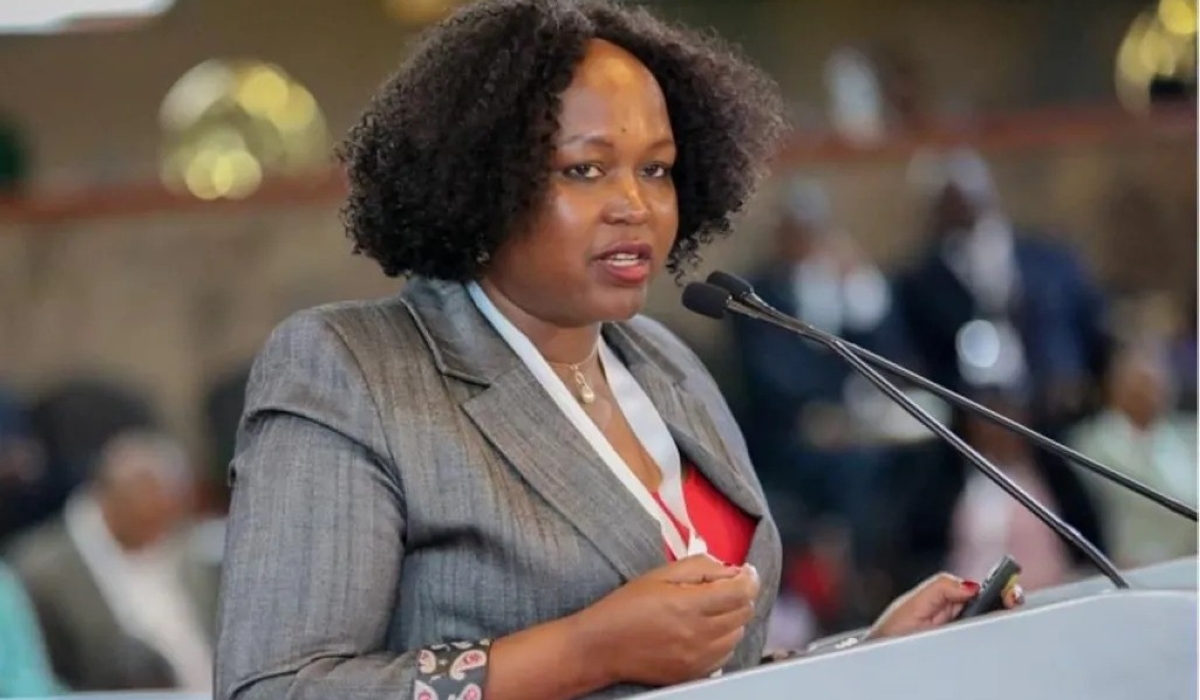
L'Autorité kenyane de lutte contre la contrefaçon (ACA) a lancé le système intégré de gestion de l'information (AIMS), un système numérique conçu pour lutter contre la contrefaçon et protéger les droits de propriété intellectuelle et les intérêts commerciaux des entreprises. Le système a été dévoilé lors de l'ouverture du deuxième symposium international sur la protection et l'application des droits de propriété intellectuelle (ISIPPE) au Kenyatta International Conference Centre (KICC) à Nairobi. Sous le thème « S'unir contre la contrefaçon pour un avenir sain et sûr », cet événement visait à renforcer la collaboration et l'innovation en matière de protection de la propriété intellectuelle, à sensibiliser aux dangers de la contrefaçon et à souligner l'importance de la sauvegarde des droits de propriété intellectuelle pour la croissance économique et la sécurité publique. Développé avec le soutien des gouvernements britannique et danois pour un coût d'environ 900 000 dollars par l'intermédiaire de TradeMark Africa (TMA), l'AIMS permet aux détenteurs de droits de propriété intellectuelle d'enregistrer leurs droits de propriété intellectuelle (marques, droits d'auteur et brevets) par l'intermédiaire d'un portail en ligne d'une grande convivialité. Cette documentation établit la propriété et sert de point de référence pour les mesures d'application. Le système dote également les organismes chargés de l'application de la loi de la capacité d'identifier et de saisir les marchandises contrefaites sur le marché ou aux points d'entrée, et ouvre la voie à des poursuites contre les contrefacteurs. Le lancement a été honoré par la presence de la secrétaire du cabinet du ministère...
L’agence kényane de lutte contre la contrefaçon dévoile un système numérique pour lutter contre les droits de propriété intellectuelle
Posted on: June 7, 2024
Posted on: June 7, 2024