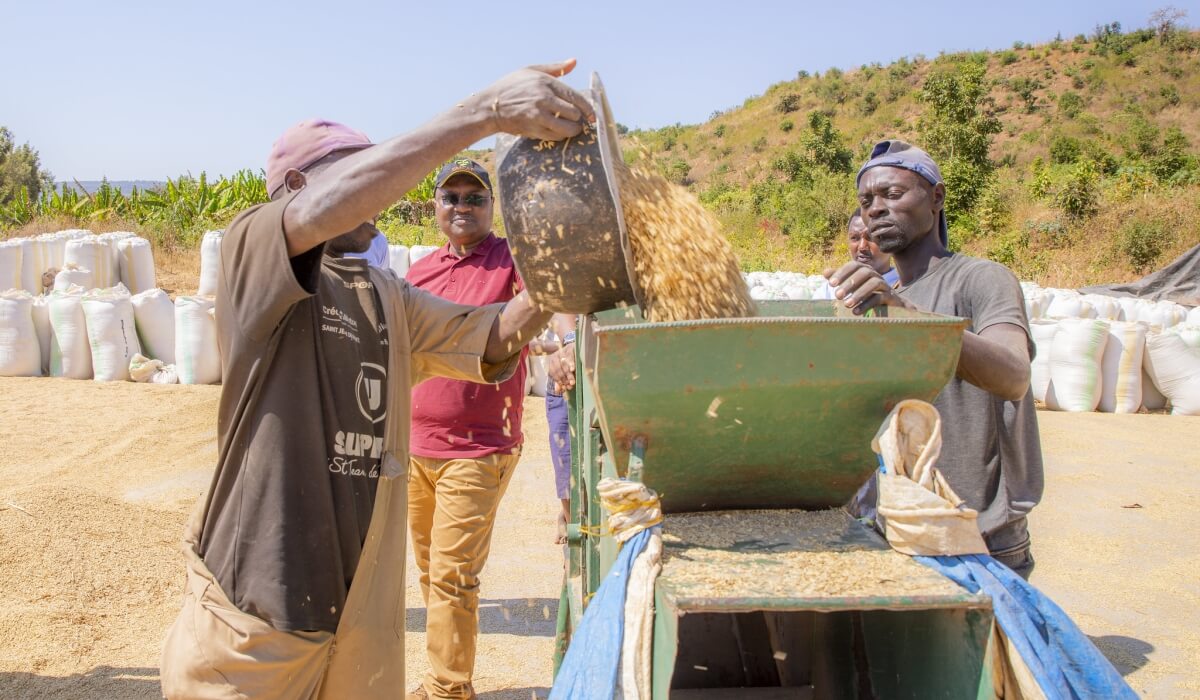
The African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) represents a historic opportunity to boost intra-regional commerce, reduce poverty, and spur Africa’s economic transformation. The World Bank estimates that AfCFTA could lift over 50 million people out of extreme poverty and raise incomes by nine per cent once fully implemented. However, realising these gains will require expanding access to financing and investment to energise trade and engage all Africans in the AfCFTA’s success. To achieve this, it is imperative to recognise that countries do not trade; people do. Therefore, there exists an urgent need to create viable avenues for trade financing that can empower individuals, entrepreneurs and businesses across the continent. The AfCFTA represents a historic opportunity to foster economic integration and create a single market for goods and services across Africa. However, the success of this ambitious initiative relies on the active participation of a multitude of actors, from small and medium enterprises to established businesses, and from rural farmers to urban entrepreneurs. Recognising that these diverse players are the true agents of trade, it becomes evident that facilitating their involvement requires a targeted approach to address the financial barriers they face. Bridging the trade finance gap A persistent challenge for African traders is limited access to the affordable financing needed for cross-border transactions and supply chain operations. The trade finance gap for Africa is estimated at over $100 billion annually. Boosting financing from both public and private sources is imperative to enable businesses of all sizes to engage in the...
Unlocking AfCFTA’s Full Potential Through Accessible Financing
Posted on: November 23, 2023
Posted on: November 23, 2023